Products with ELD "EMpt30"
- ELDMANDATE-(Android-ELM327) Version 1.0.1905.190710 & up
- ELDMANDATE-(Android-Geometris) Version 1.0.1905.190710
- ELDMANDATE-HOS Version 1.0.1905.190710 & up
- ELDMANDATE-HOS Version 3.0.2116.210920
- ELDMANDATE-HOS Version 3.0.2212.220822
Below you will find a list of products with the ELD "" obtained from our database, including their available manuals, documentation, and images.
Click the corresponding vendor name to obtain additional information on the manufactorer, as well as contact information for further troubleshooting.
ELDMANDATE (Android ELM327) - Self Revoked as of 1576441615

| Vendor | Device Name | Model Number | Approved Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| | ELDMANDATE (Android ELM327) | LBT26017 | 1.0.1905.190710 & up |
Data Transfer and Reporting Procedures
>Malfunctions and Testing
The LB Technology HOS provides a standardized single-step compilation for the driver’s ELD records and initiation of the data transfer to authorized safety officials when requested during a roadside inspection. Selecting the Data Transfer button from the Main HOS Main Screen will display the list of supported data transfer options which are via Bluetooth, Email, and USB. A Select Vehicle option is also available for selecting a vehicle upon performing the data transfer, this option enables the LB Technology HOS to produce a data file or a series of data files of ELD records for a subset of its vehicles used by the driver. • Transfer via Bluetooth - this option enables the user to transfer files through Bluetooth. The ELD prompts for an output file comment which the driver may enter (optional). After the input, if Bluetooth is not yet turned on, a prompt will appear asking you to turn it on. You will then be asked to select the device name to which the data will be transmitted via Bluetooth. • Transfer via Email - this option enables the user to transfer files through email. The ELD output file transferred is encrypted using AES-256 in FIPS Publication 197. Before sending, the ELD prompts for an output file comment which the driver may enter (optional). The device's default email application will then be opened before sending the email to which the data will be transferred. • Transfer via USB - this option enables the user to transfer files through USB (external devices). However, prior to saving the driver’s ELD file to an external storage/device, the ELD re-authenticates the driver account by asking for its password.Certification Statement
The LB Technology's HOS ELD is capable of monitoring its compliance for various detectable malfunctions. At each instance when an ELD malfunction event is detected or cleared by the LB Technology HOS ELD, the ELD records the event. The recorded malfunction events are inconsistencies found while monitoring the ELD against FMCSA compliance requirements. Malfunction occurrences are indicated in the application header and in the Android notification toolbar with the letter ‘M’, respectively. The following shows the list of detectable malfunctions: • Power Malfunction • Engine Synchronization Malfunction • Timing Malfunction • Position Malfunction • Data Recording Malfunction • Data Transfer Malfunction Once the Malfunctions indicator ‘M’ is tapped, a dialog will be displayed with a list of the detected malfunction events alongside a ‘Clear’ button for each event. Tapping the Clear button will clear out the detected malfunction event.
ELDMANDATE (Android Geometris) - Self Revoked as of 1576441597

| Vendor | Device Name | Model Number | Approved Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| | ELDMANDATE (Android Geometris) | LBT26018 | 1.0.1905.190710 |
Data Transfer and Reporting Procedures
>Malfunctions and Testing
The LB Technology HOS provides a standardized single-step compilation for the driver’s ELD records and initiation of the data transfer to authorized safety officials when requested during a roadside inspection. Selecting the Data Transfer button from the Main HOS Main Screen will display the list of supported data transfer options which are via Bluetooth, Email, and USB. A Select Vehicle option is also available for selecting a vehicle upon performing the data transfer, this option enables the LB Technology HOS to produce a data file or a series of data files of ELD records for a subset of its vehicles used by the driver. • Transfer via Bluetooth - this option enables the user to transfer files through Bluetooth. The ELD prompts for an output file comment which the driver may enter (optional). After the input, if Bluetooth is not yet turned on, a prompt will appear asking you to turn it on. You will then be asked to select the device name to which the data will be transmitted via Bluetooth. • Transfer via Email - this option enables the user to transfer files through email. The ELD output file transferred is encrypted using AES-256 in FIPS Publication 197. Before sending, the ELD prompts for an output file comment which the driver may enter (optional). The device's default email application will then be opened before sending the email to which the data will be transferred. • Transfer via USB - this option enables the user to transfer files through USB (external devices). However, prior to saving the driver’s ELD file to an external storage/device, the ELD re-authenticates the driver account by asking for its password.Certification Statement
The LB Technology's HOS ELD is capable of monitoring its compliance for various detectable malfunctions. At each instance when an ELD malfunction event is detected or cleared by the LB Technology HOS ELD, the ELD records the event. The recorded malfunction events are inconsistencies found while monitoring the ELD against FMCSA compliance requirements. Malfunction occurrences are indicated in the application header and in the Android notification toolbar with the letter ‘M’, respectively. The following shows the list of detectable malfunctions: • Power Malfunction • Engine Synchronization Malfunction • Timing Malfunction • Position Malfunction • Data Recording Malfunction • Data Transfer Malfunction Once the Malfunctions indicator ‘M’ is tapped, a dialog will be displayed with a list of the detected malfunction events alongside a ‘Clear’ button for each event. Tapping the Clear button will clear out the detected malfunction event.
ELDMANDATE HOS
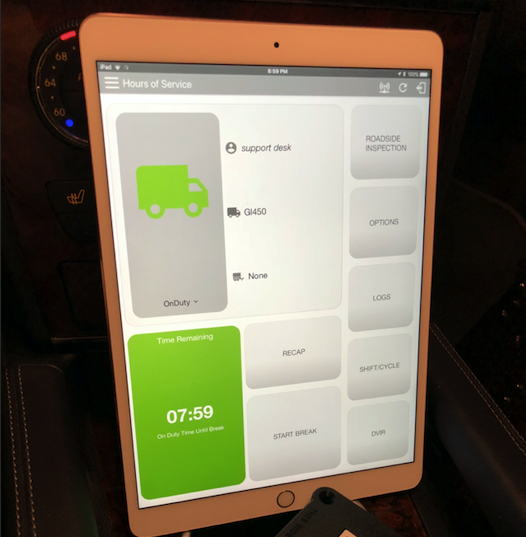
| Vendor | Device Name | Model Number | Approved Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| | ELDMANDATE HOS | EMPT30 | 1.0.1905.190710 & up |
Data Transfer and Reporting Procedures
The ELDMANDATE HOS provides a standardized single-step compilation for the driver’s ELD records and initiation of the data transfer to authorized safety officials when requested during a roadside inspection. Selecting the Data Transfer button from the Main HOS Main Screen will display the list of supported data transfer options which are via Bluetooth, Email, and USB. A Select Vehicle option is also available for selecting a vehicle upon performing the data transfer, this option enables the ELDMANDATE HOS to produce a data file or a series of data files of ELD records for a subset of its vehicles used by the driver. • Transfer via Bluetooth - this option enables the user to transfer files through Bluetooth. The ELD prompts for an output file comment which the driver may enter (optional). After the input, if Bluetooth is not yet turned on, a prompt will appear asking you to turn it on. You will then be asked to select the device name to which the data will be transmitted via Bluetooth. • Transfer via Email - this option enables the user to transfer files through email. The ELD output file transferred is encrypted using AES-256 in FIPS Publication 197. Before sending, the ELD prompts for an output file comment which the driver may enter (optional). The device's default email application will then be opened before sending the email to which the data will be transferred. • Transfer via USB - this option enables the user to transfer files through USB (external devices). However, prior to saving the driver’s ELD file to an external storage/device, the ELD re-authenticates the driver account by asking for its passwordMalfunctions and Testing
The ELDMANDATE HOS ELD is capable of monitoring its compliance for various detectable malfunctions. At each instance when an ELD malfunction event is detected or cleared by the ELDMANDATE HOS ELD, the ELD records the event. The recorded malfunction events are inconsistencies found while monitoring the ELD against FMCSA compliance requirements. Malfunction occurrences are indicated in the application header and in the Android notification toolbar with the letter ‘M’, respectively. The following shows the list of detectable malfunctions: • Power Malfunction • Engine Synchronization Malfunction • Timing Malfunction • Position Malfunction • Data Recording Malfunction • Data Transfer Malfunction Once the Malfunctions indicator ‘M’ is tapped, a dialog will be displayed with a list of the detected malfunction events alongside a ‘Clear’ button for each event. Tapping the Clear button will clear out the detected malfunction event. Procedure to validate an ELD authentication value 1. Concatenate the driver license number, ELD identifier, and ELD registration ID together. If there is no driver’s license number use the empty string for the driver license number. 2. Hash the value from step 1 using SHA-256. 3. Get the provider's public certificate in ASN.1 DER encoded form as a byte array. 4. Concatenate the byte array from step 2 with the byte array from step 3. 5. Hash the value from step 4 using SHA-256. 6. Take the first 16 bytes from the byte array in step 5 and convert the bytes into a hex string. The resulting 32-character string is the authentication value Certifying Statment of FMCSA Regulation Testing The ELDMANDATE ELD was certified through successful execution and verification of the FMCSA ELD Test Procedures. The ELDMANDATE ELD was installed on various types and sizes of Android phones and tablets. Testing was performed using a J1939 simulator and actual vehicles while having been connected to the hardware device. A few of the test procedures, which are relevant to Motor Carriers, were verified using the Hours of Service web application (portal) that can be accessed through a web browser.Certification Statement
The ELDMANDATE ELD was certified through successful execution and verification of the FMCSA ELD Test Procedures. The ELDMANDATE ELD was installed on various types and sizes of Android phones and Apple iOS phones and tablets. Testing was performed using a J1939 simulator and actual vehicles while having been connected to the hardware device. A few of the test procedures, which are relevant to Motor Carriers, were verified using the Hours of Service web application (portal) that can be accessed through a web browser.
ELDMANDATE HOS

| Vendor | Device Name | Model Number | Approved Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| | ELDMANDATE HOS | EMPT30 | 3.0.2116.210920 |
Data Transfer and Reporting Procedures
The ELDMANDATE HOS provides a standardized single-step compilation for the driver’s ELD records and initiation of the data transfer to authorized safety officials when requested during a roadside inspection. Selecting the Data Transfer button from the Main HOS Main Screen will display the list of supported data transfer options which are via Bluetooth, Email, and USB. A Select Vehicle option is also available for selecting a vehicle upon performing the data transfer, this option enables the ELDMANDATE HOS to produce a data file or a series of data files of ELD records for a subset of its vehicles used by the driver. • Transfer via Bluetooth - this option enables the user to transfer files through Bluetooth. The ELD prompts for an output file comment which the driver may enter (optional). After the input, if Bluetooth is not yet turned on, a prompt will appear asking you to turn it on. You will then be asked to select the device name to which the data will be transmitted via Bluetooth. • Transfer via Email - this option enables the user to transfer files through email. The ELD output file transferred is encrypted using AES-256 in FIPS Publication 197. Before sending, the ELD prompts for an output file comment which the driver may enter (optional). The device's default email application will then be opened before sending the email to which the data will be transferred. • Transfer via USB - this option enables the user to transfer files through USB (external devices). However, prior to saving the driver’s ELD file to an external storage/device, the ELD re-authenticates the driver account by asking for its passwordMalfunctions and Testing
The ELDMANDATE HOS ELD is capable of monitoring its compliance for various detectable malfunctions. At each instance when an ELD malfunction event is detected or cleared by the ELDMANDATE HOS ELD, the ELD records the event. The recorded malfunction events are inconsistencies found while monitoring the ELD against FMCSA compliance requirements. Malfunction occurrences are indicated in the application header and in the Android notification toolbar with the letter ‘M’, respectively. The following shows the list of detectable malfunctions: • Power Malfunction • Engine Synchronization Malfunction • Timing Malfunction • Position Malfunction • Data Recording Malfunction • Data Transfer Malfunction Once the Malfunctions indicator ‘M’ is tapped, a dialog will be displayed with a list of the detected malfunction events alongside a ‘Clear’ button for each event. Tapping the Clear button will clear out the detected malfunction event. Procedure to validate an ELD authentication value 1. Concatenate the driver license number, ELD identifier, and ELD registration ID together. If there is no driver’s license number use the empty string for the driver license number. 2. Hash the value from step 1 using SHA-256. 3. Get the provider's public certificate in ASN.1 DER encoded form as a byte array. 4. Concatenate the byte array from step 2 with the byte array from step 3. 5. Hash the value from step 4 using SHA-256. 6. Take the first 16 bytes from the byte array in step 5 and convert the bytes into a hex string. The resulting 32-character string is the authentication value Certifying Statment of FMCSA Regulation Testing The ELDMANDATE ELD was certified through successful execution and verification of the FMCSA ELD Test Procedures. The ELDMANDATE ELD was installed on various types and sizes of Android phones and tablets. Testing was performed using a J1939 simulator and actual vehicles while having been connected to the hardware device. A few of the test procedures, which are relevant to Motor Carriers, were verified using the Hours of Service web application (portal) that can be accessed through a web browser.Certification Statement
The ELDMANDATE ELD was certified through successful execution and verification of the FMCSA ELD Test Procedures. The ELDMANDATE ELD was installed on various types and sizes of Android phones and Apple iOS phones and tablets. Testing was performed using a J1939 simulator and actual vehicles while having been connected to the hardware device. A few of the test procedures, which are relevant to Motor Carriers, were verified using the Hours of Service web application (portal) that can be accessed through a web browser.
ELDMANDATE HOS

| Vendor | Device Name | Model Number | Approved Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| | ELDMANDATE HOS | EMPT30 | 3.0.2212.220822 |
Data Transfer and Reporting Procedures
> Telematic (Web Service, Email)Malfunctions and Testing
HOS application uses web services and email transmission for data transferCertification Statement
At each instance when an ELD malfunction event is detected or cleared by the software, the ELD records the event. The recorded malfunction events are inconsistencies found while monitoring the ELD against FMCSA compliance requirements. Malfunction occurrences are indicated in the application header and in the notification toolbar with an alert sign, respectively. The following shows the list of detectable malfunctions: - Power data diagnostic (diagnostic - 1) - Engine synchronization data diagnostic (diagnostic - 2) - Missing required data elements (diagnostic - 3) - Data transfer (diagnostic - 4) - Unidentified driving records data diagnostic (diagnostic - 5) - Power compliance (malfunction - P) - Engine synchronization compliance (malfunction - E) - Timing compliance (malfunction - T) - Positioning compliance (malfunction - L) - Data recording compliance (malfunction - R) - Data transfer compliance (malfunction - S) When the user is presented with this, he is able to rectify the situation, contact the manufacturer or use paper logs to remain compliant. The malfunctions and diagnostic codes can be found in the instruction guide with the required details in order for the driver to understand it.